In today's digital landscape, Linux SSH servers have become prime targets for hackers due to their widespread use in hosting critical services. This article explores the various vulnerabilities that make these servers susceptible to unauthorized access and potential exploitation. From weak passwords to unpatched vulnerabilities and misconfigurations, there are several loopholes that threat actors exploit. Recent research by AhnLab Security Emergency Response Center (ASEC) reveals that hackers are actively attacking Linux SSH servers to deploy scanner malware. By targeting poorly managed servers, they aim to obtain IP addresses and SSH credentials for malicious activities such as DDoS attacks and cryptocurrency mining. To achieve their goals, hackers employ techniques like IP scanning, brute force attacks, and the installation of malware such as ShellBot, Tsunami, and Mirai. This article provides essential mitigations to safeguard your cybersecurity, including using strong and regularly changed passwords, regularly updating patches, employing firewalls, and exercising caution with security versions. By implementing these strategies, you can enhance the security of your Linux SSH servers and protect your critical services from potential threats.
The Vulnerabilities of Linux SSH Servers
Linux SSH servers are widely used for hosting critical services, making them attractive targets for hackers. Weak passwords, unpatched vulnerabilities, and misconfigurations are common loopholes that threat actors exploit. By understanding these vulnerabilities, you can take proactive measures to protect your servers.
Weak Passwords: Many server administrators neglect the importance of strong passwords, leaving their servers vulnerable to brute force attacks. It is crucial to use complex passwords that include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
Unpatched Vulnerabilities: Failing to regularly update patches and security fixes exposes servers to known vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit. Stay up to date with the latest patches and security updates to minimize the risk.
Misconfigurations: Improperly configuring SSH servers can create security gaps that hackers can exploit. It is essential to follow best practices and configure servers securely to prevent unauthorized access.
Scanner Malware: A Growing Threat
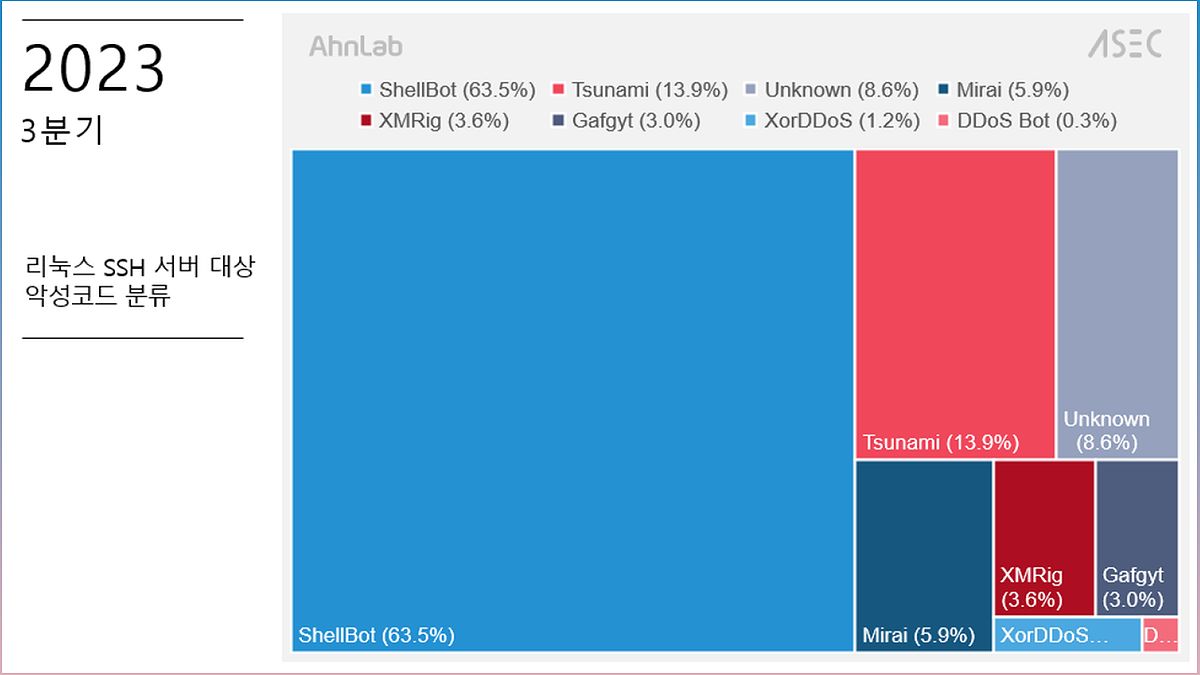
Recent research has revealed a rise in hacker attacks targeting Linux SSH servers using scanner malware. These malicious programs are designed to scan for vulnerable servers and gather IP addresses and SSH credentials for further exploitation.
Threat actors use techniques like IP scanning and brute force attacks to identify active SSH ports and gain unauthorized access. Once inside, they can deploy additional malware such as DDoS bots and CoinMiners, which can cause significant damage to your server and compromise its performance.
It is crucial to be aware of this growing threat and take proactive measures to protect your Linux SSH servers from scanner malware. Implementing strong security measures, such as regularly updating patches, using intrusion detection systems, and monitoring network traffic, can help mitigate the risks.
Common Malware Targeting Linux SSH Servers
Hackers often install various types of malware on Linux SSH servers after gaining unauthorized access. Some of the most common malware include:
ShellBot:
A sophisticated botnet that can perform DDoS attacks, spread malware, and launch brute force attacks.
Tsunami:
A powerful DDoS bot that can create a massive volume of network traffic, overwhelming servers and causing service disruptions.
Mirai:
A notorious botnet that targets IoT devices, including Linux SSH servers, to carry out large-scale DDoS attacks.
These malware can have severe consequences for your server's security and performance. It is essential to implement robust security measures and regularly monitor your server for any signs of compromise.
Mitigating Vulnerabilities: Best Practices for Cybersecurity
To enhance the security of your Linux SSH servers, it is crucial to follow these best practices:
- Use Strong and Regularly Changed Passwords: Implement complex passwords and regularly update them to minimize the risk of brute force attacks.
- Regularly Update Patches: Stay up to date with the latest patches and security updates to address known vulnerabilities.
- Employ Firewalls: Use firewalls to filter network traffic and protect your server from unauthorized access.
- Exercise Caution with Security Versions: Be cautious when using new security versions, as they may have vulnerabilities that threat actors can exploit. It is important to thoroughly test and evaluate new versions before implementation.
By implementing these strategies, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and potential exploitation of your Linux SSH servers.